During fiber laser cutting of metal sheets, the laser beam’s instantaneous high temperature can easily cut through metal, but excessive heat can lead to poor cutting quality. For example, when cutting thick plates that require auxiliary gases, if the gas pressure is too high or too low, excessive heat input can cause slagging. Similarly, when cutting small round holes, the confined space for heat propagation can cause excessive heat to concentrate in a small area, which also easily results in slagging.
Different customers have varying requirements for the quality of cut surfaces and the degree of processing. If slagging occurs, the following steps can be taken for troubleshooting and adjustment.
01 Check Output Power
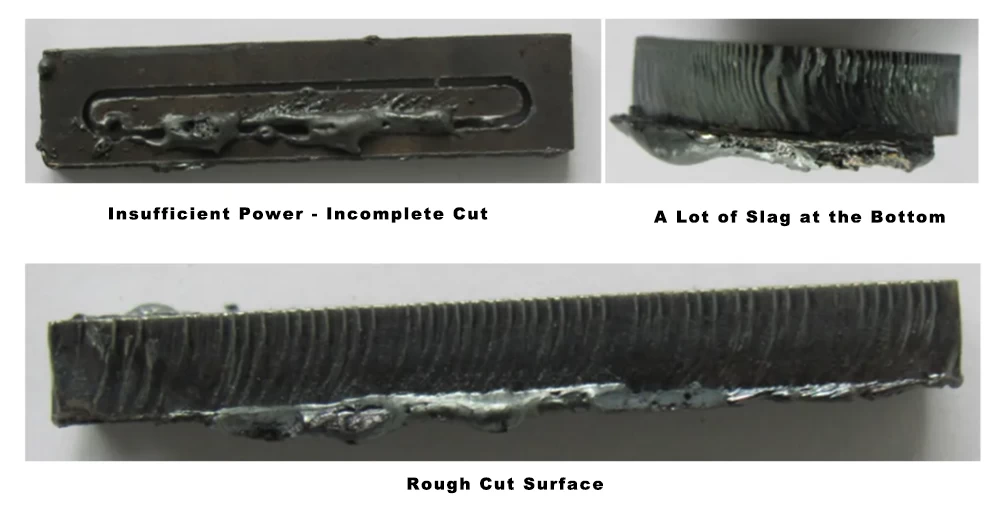
In laser cutting, if the output power is too low, it will lead to failure to cut or incomplete cutting, resulting in melt stains and scars on the cut cross section; when the power is too high, the cut surface melt slit is too large and excellent cutting quality cannot be obtained.
The following figure shows the problems that occur when cutting mild steel plates when the laser power is insufficient.
02 Check Gas Pressure
In laser cutting, auxiliary gases (commonly O₂, compressed air, N₂, and rare gases) are used to blow away molten slag and cool the heat-affected zone during cutting.
Most metals are processed using active gases like O₂, as O₂ can oxidize the metal surface, improving cutting efficiency. However, if the auxiliary gas pressure is too high, eddy currents appear on the surface of the material, weakening the ability to remove the molten material, causing the kerf to become wider and the cutting surface to become rough. If the pressure is too low, the molten material cannot be completely blown away, leading to slag adhering to the underside of the material.
03 Check Focus Position
The focus position refers to the distance between the laser focus and the surface of the workpiece. It directly affects the roughness of the cut surface, the slope, and width of the cut.
If the focus is too far ahead, more heat will be absorbed by the lower part of the workpiece. Under constant cutting speed and gas pressure, the molten material and material near the cut seam may flow as liquid onto the underside, and after cooling, the molten material forms spherical slag on the underside. If the focus is too far behind, the heat absorbed by the bottom of the material is reduced, causing incomplete melting of the material and resulting in sharp, small slag adhering to the underside.

04 Check Cutting Speed
The cutting speed in laser cutting is determined by the material and thickness of the plate. The choice of cutting speed greatly impacts the cutting quality. Selecting the right speed improves both the cutting efficiency and quality.
Improper cutting speed will cause cutting defects as shown in the figure below:

Conclusion
Slagging is a common issue in laser cutting that affects cutting quality. By adjusting output power, gas pressure, focus position, and cutting speed, slagging can be effectively avoided or minimized, thereby improving cutting performance and efficiency. During troubleshooting, adjust each factor to ensure optimal cutting quality.
Share The Post Now:
You Might Also Like
Yupec Laser is a leading provider of advanced fiber laser solutions in Europe, specializing in the sales, technical support, and service of Raycus fiber lasers.
With years of experience and a team of industry experts, we will be happy to help you with all your laser and laser application needs.
For more information about our products and services, please feel free to get in touch with us. We look forward to collaborating with you and driving innovation together.







